3-Year vs 5-Year MH-CET Law: Preparation and Cut-Off Differences Explained
Introduction: One Exam Name, Two Very Different Journeys
MH-CET Law is conducted for two distinct courses:
- 3-Year LL.B.
- 5-Year Integrated LL.B.
Many aspirants assume that the preparation strategy and cut-off logic are almost the same for both. This assumption often leads to a misguided focus on preparation, unrealistic expectations, and post-result disappointment.
In reality, although the exam pattern may appear similar on paper, the competition profile, preparation depth, and cut-off behavior differ significantly between the 3-Year and 5-Year MH-CET Law exams.
This article explains those differences clearly so aspirants can prepare with the right mindset.
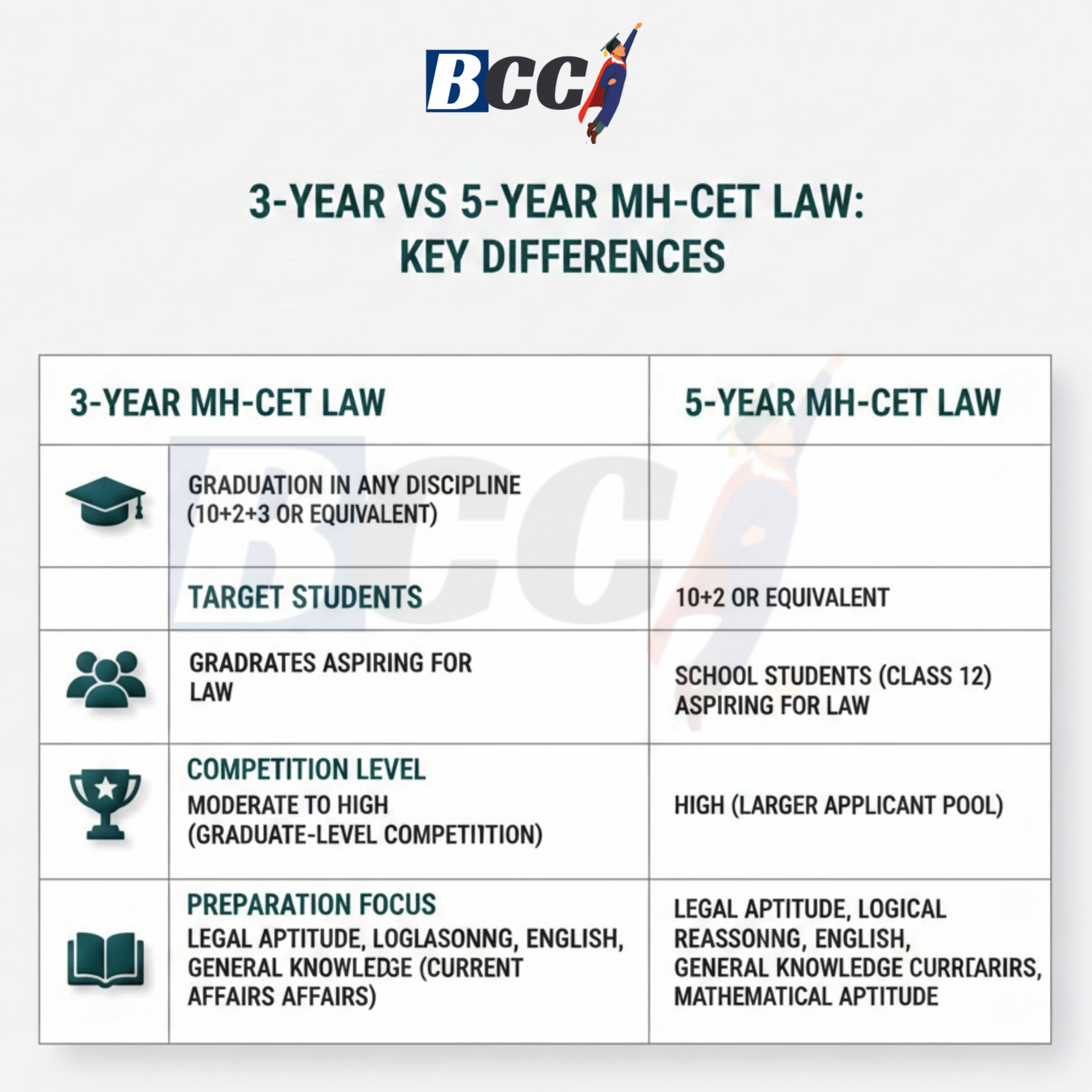
Basic Difference Between 3-Year and 5-Year MH-CET Law
| Aspect | 3-Year MH-CET Law | 5-Year MH-CET Law |
|---|---|---|
| Target group | Graduates | Class 12 students |
| Average age | Higher | Lower |
| Competition type | Mature, repeat-heavy | Large volume, first-time |
| Attempt maturity | High | Mixed |
Understanding this base difference is important before comparing preparation and cut-offs.
Syllabus Depth: Similar Topics, Different Expectations
Legal Aptitude
- 5-Year CET:
Focuses on basic legal principles, comprehension, and simple application. - 3-Year CET:
Questions are conceptually similar but expect better understanding and accuracy.
Logical Reasoning
- 5-Year CET:
Speed-based, pattern recognition, simpler logic. - 3-Year CET:
Slightly more analytical, fewer guess-based questions.
GK & Current Affairs
- 5-Year CET:
Often ignored by students, becomes a rank-decider. - 3-Year CET:
Better prepared candidate pool, GK matters more consistently.
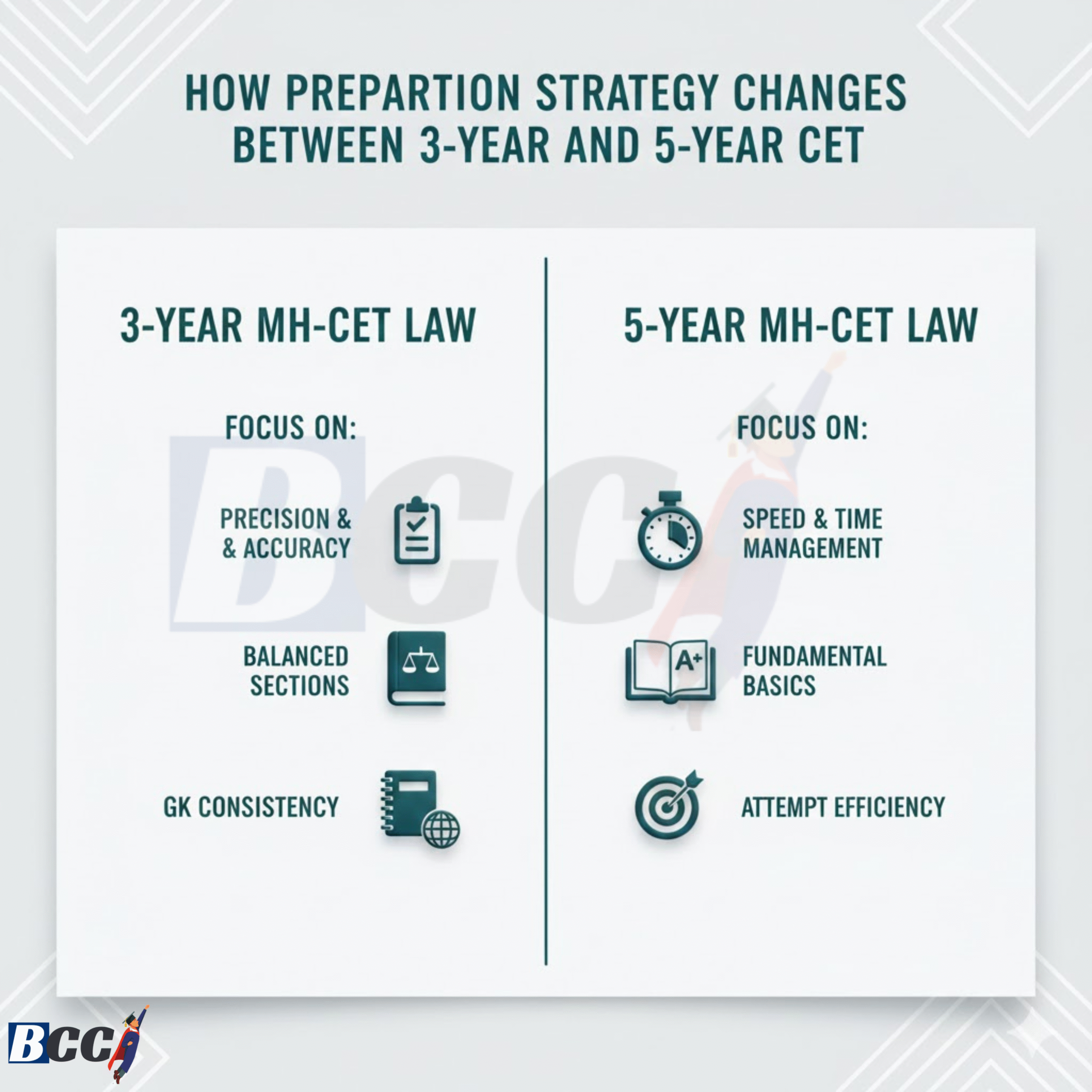
Preparation Approach: What Changes Between 3-Year and 5-Year
5-Year MH-CET Law Preparation
- Aspirants are mostly school students
- Many are first-time competitive exam takers
- Coaching exposure varies widely
Preparation focus should be on:
- Speed building
- Basic concept clarity
- Legal Aptitude accuracy
- Avoiding silly mistakes
3-Year MH-CET Law Preparation
- Aspirants are graduates
- Many are repeat law entrance candidates
- Competition quality is higher
Preparation focus should be on:
- Precision over speed
- Section-wise balance
- GK consistency
- Rank-oriented strategy
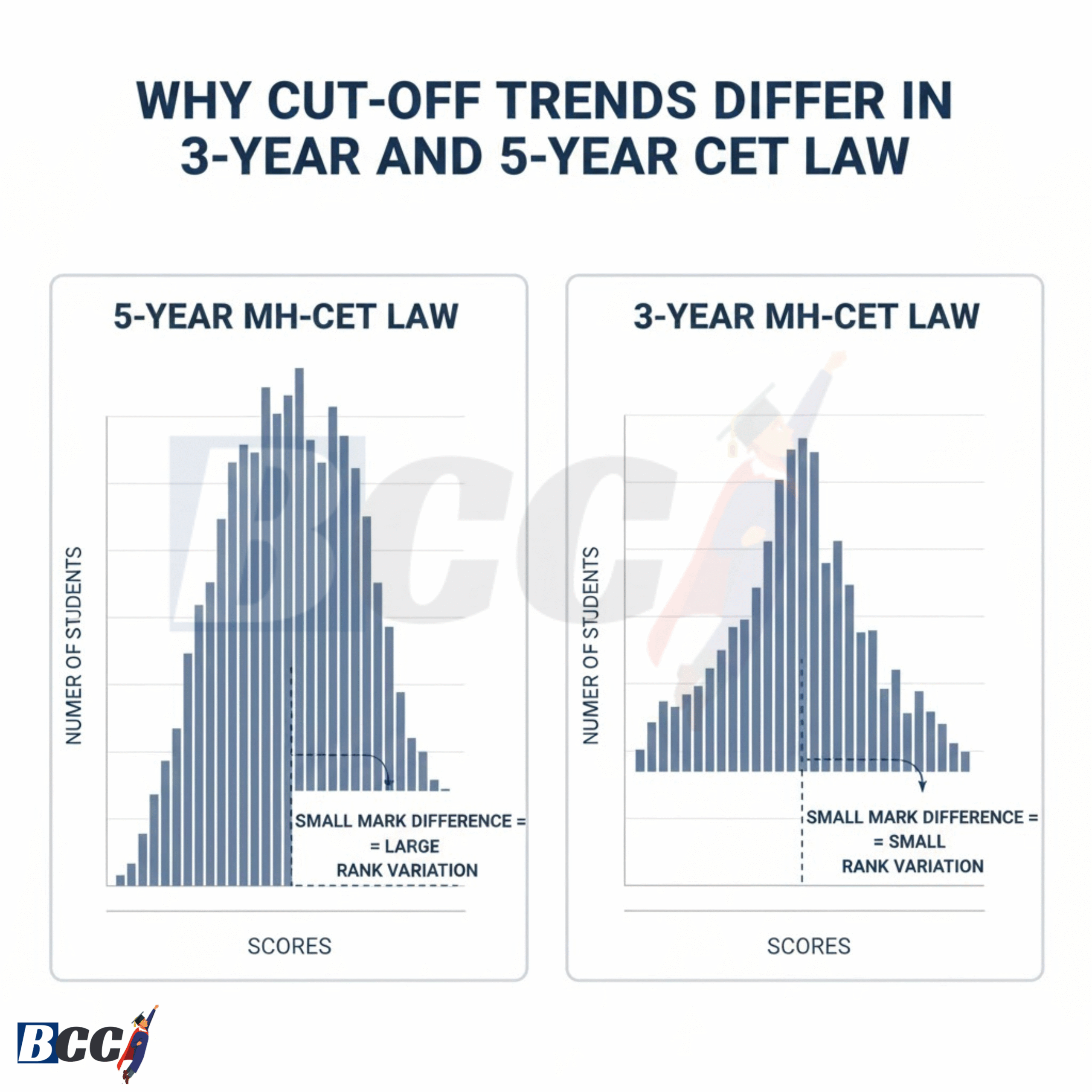
Cut-Off Behaviour: Why They Differ
5-Year MH-CET Law Cut-Offs
- Generally higher in marks
- Paper often feels easy
- A large number of candidates score similarly
- Small mistakes cause big rank drops
Because of high volume and score density, cut-offs for top colleges remain competitive despite easy papers.
3-Year MH-CET Law Cut-Offs
- Slightly lower marks compared to the 5-Year
- Competition is narrower but sharper
- Aspirants are better prepared overall
Here, cut-offs are influenced more by relative ranking among serious candidates than by paper difficulty.
Rank vs Marks: Difference in Impact
In both exams, merit rank matters more than marks, but the effect varies.
- In 5-Year CET, a 1–2 mark difference can shift rank by hundreds.
- In 3-Year CET, even a single mistake can change college allotment due to tight competition.
This is why aspirants must judge performance based on expected rank, not raw marks.
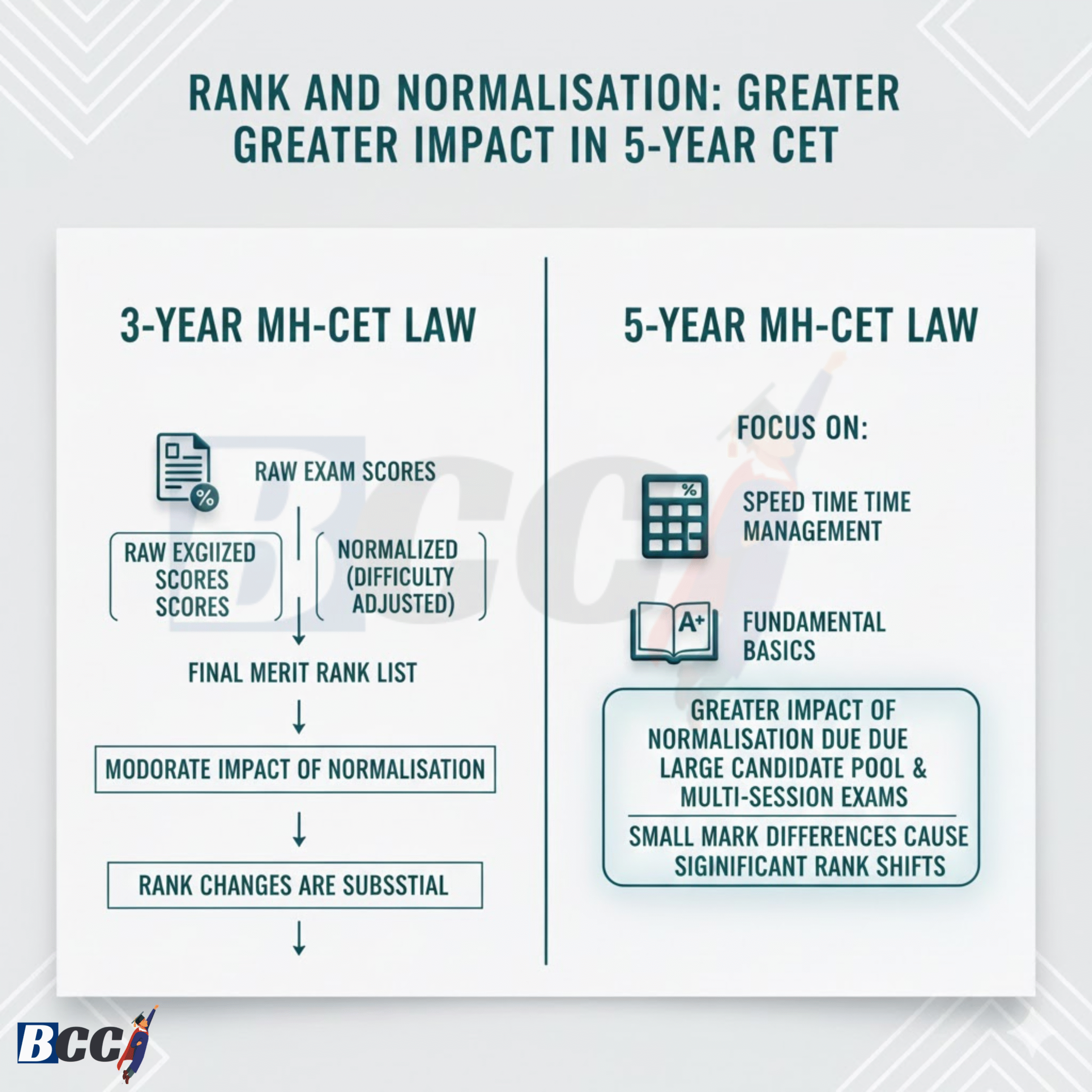
Normalisation Impact: More Visible in 5-Year CET
- 5-Year CET is usually conducted in multiple shifts
- Normalisation plays a bigger role
- Easy shifts often see higher average scores
As a result, many students with “good marks” still get lower-than-expected ranks.
In 3-Year CET, shifts are fewer and competition is more uniform, so the normalisation impact is comparatively subtle.
College Preference Pressure: Where It Hurts More
5-Year CET
- More colleges
- More seats
- But the extremely high demand for top colleges
Wrong preference filling can cost a better college, even with a decent rank.
3-Year CET
- Fewer colleges
- Limited seats
- Higher pressure on the rank
Here, a realistic preference strategy is as important as exam performance.
Common Preparation Mistakes (Exam-Wise)
Mistakes in 5-Year CET Preparation
- Ignoring GK completely
- Overconfidence due to easy mocks
- Poor time management
Mistakes in 3-Year CET Preparation
- Assuming graduation knowledge is enough
- Neglecting Legal Aptitude revision
- Underestimating competition quality
What Aspirants Should Do Differently
If You Are Preparing for 5-Year CET:
- Focus on speed + accuracy
- Strengthen Legal Aptitude basics
- Don’t ignore GK
- Practice mock analysis seriously
If You Are Preparing for 3-Year CET:
- Aim for precision
- Avoid silly mistakes
- Balance all sections
- Prepare with rank targets in mind
Which Exam Is “Tougher”?
This is the wrong question.
- 5-Year CET is tougher due to volume and score density
- 3-Year CET is tougher due to the competition quality
Difficulty lies in who you are competing against, not how hard the paper looks.
Conclusion: Same Exam Name, Different Strategy
3-Year and 5-Year MH-CET Law exams may look similar, but preparation strategy, competition behaviour, and cut-off logic are clearly different.
Aspirants who understand these differences early:
- Prepare more realistically
- Avoid post-result confusion
- Make better college decisions
The key is not working harder—but preparing in alignment with the specific CET you are targeting.
Frequently Asked Questions (MH-CET Law 3-Year vs 5-Year)
1. Is the MH-CET Law syllabus different for 3-Year and 5-Year exams?
The syllabus topics are broadly similar, but the level of competition and expected accuracy differ. The 3-Year exam requires more precision, while the 5-Year exam focuses more on speed and basic concept clarity.
2. Which MH-CET Law exam has higher cut-offs: 3-Year or 5-Year?
Generally, the 5-Year MH-CET Law shows higher cut-offs due to a larger number of candidates and score density. The 3-Year exam has slightly lower cut-offs but sharper competition.
3. Does normalisation affect both 3-Year and 5-Year CET Law equally?
Normalisation affects both, but its impact is usually more visible in the 5-Year CET because it is conducted in multiple shifts with varied difficulty levels.
4. Can I prepare for 3-Year and 5-Year MH-CET Law together?
Basic preparation can overlap, but the strategy must differ. Aspirants should adjust speed, accuracy, and section focus depending on the exam they are targeting.
5. Which section matters most for MH-CET Law cut-offs?
Legal Aptitude is the most important section for both exams. However, GK and Logical Reasoning often decide rank when scores are closely clustered.